4 of 6: A six (6) Article Series On The Evolution of the Automobile, From ICE to EV Powered Vehicles by 2035, The Transformation Years and Dependence on Lithium Powered Batteries!
Introduction: The automobile industry, a cornerstone of modern society, has faced significant challenges and undergone remarkable transformations over the past few decades. Environmental concerns and technological advances have driven this evolution, shaping the future of transportation. This article explores the industry’s response to environmental challenges, the development of hybrid and electric vehicles, the push for sustainability, and the prospects of autonomous driving, providing a comprehensive look at how the automobile industry continues to innovate and adapt.
Chapter 1: The Rise of Environmental Awareness In the late 20th century, growing awareness of environmental issues, particularly air pollution and climate change, prompted significant scrutiny of the automobile industry. Automobiles were identified as major contributors to greenhouse gas emissions and urban smog. Governments and environmental organizations began to push for stricter emissions standards and cleaner technologies.

The Oil Crises and Fuel Efficiency The oil crises of the 1970s had already highlighted the vulnerabilities of an oil-dependent economy, prompting initial efforts toward improving fuel efficiency. The Corporate Average Fuel Economy (CAFE) standards, introduced in the United States in 1975, required automakers to achieve specific fuel efficiency targets, driving innovation in engine technology and vehicle design.
Chapter 2: The Advent of Hybrid Vehicles The first significant technological response to these challenges was the development of hybrid vehicles. Combining a traditional internal combustion engine with an electric motor, hybrids offered improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions.

Call me for a free estimate in the Greater Montreal Area.
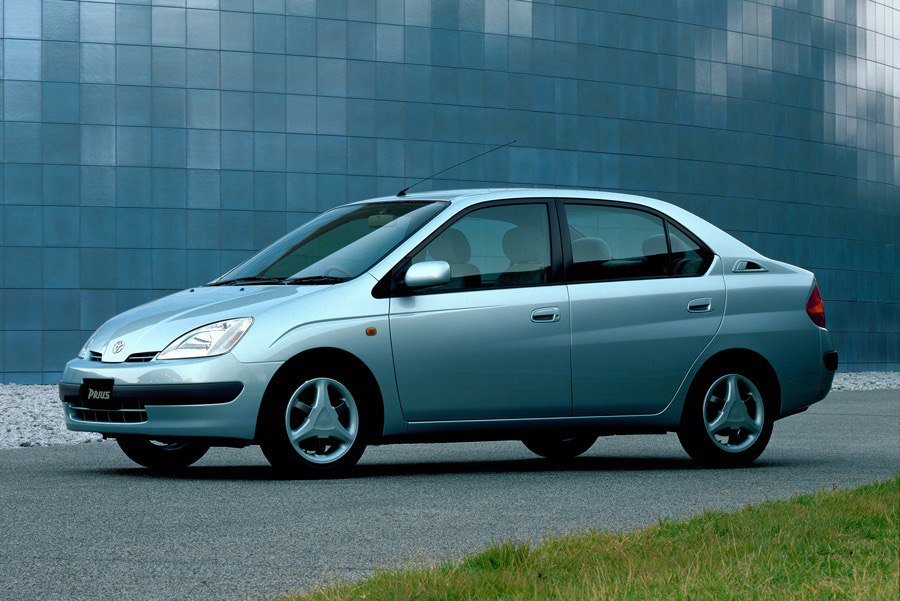
Toyota Prius: A Milestone in Automotive History The Toyota Prius, introduced in Japan in 1997 and globally in 2000, became the world’s first mass-produced hybrid vehicle. Its success was a game-changer, proving that consumers were ready for environmentally friendly alternatives. The Prius’ efficient use of regenerative braking and advanced battery technology set a new standard for automotive innovation.
CLICK ON IMAGE FOR MORE INFORMATION
Other Pioneers in Hybrid Technology Following Toyota’s lead, other manufacturers developed their own hybrid models. Honda introduced the Insight, while Ford, General Motors, and European carmakers launched various hybrid versions of popular models. These vehicles demonstrated the potential for significant reductions in fuel consumption and emissions without sacrificing performance or convenience.
Chapter 3: The Electric Vehicle Revolution Building on the success of hybrids, the next major leap in automotive technology was the development of fully electric vehicles (EVs). Unlike hybrids, EVs rely entirely on electric power, producing zero tailpipe emissions.
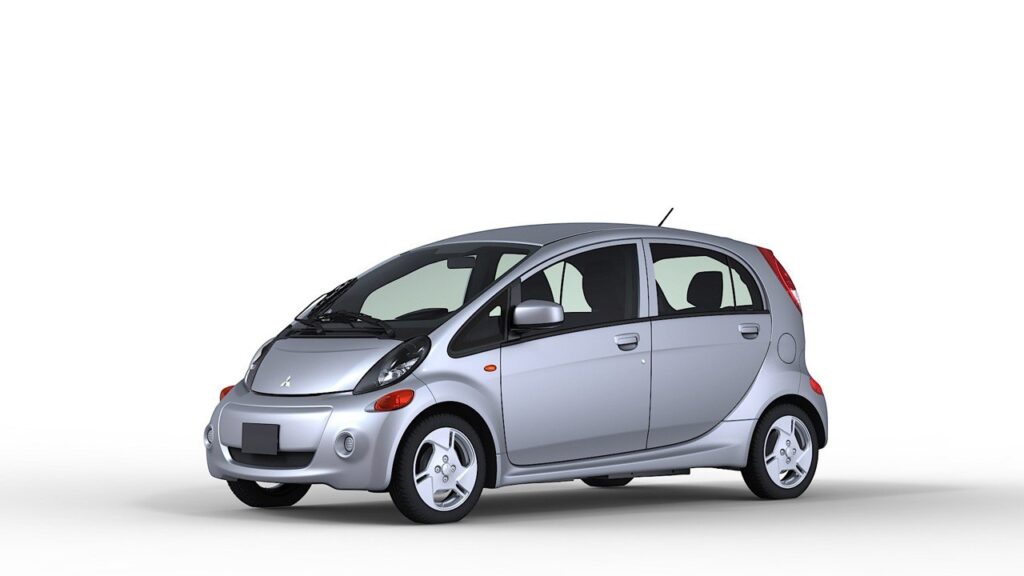
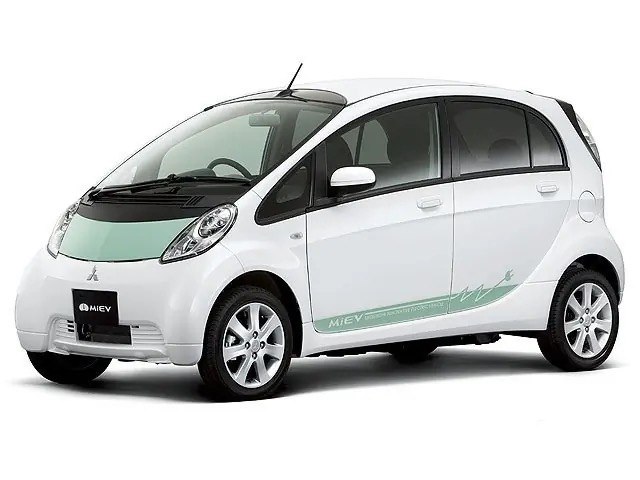
Early Pioneers: Mitsubishi’s Contribution Mitsubishi Motors has been at the forefront of EV technology development for decades. In 2009, Mitsubishi launched the i-MiEV (Mitsubishi Innovative Electric Vehicle), which became the first highway-legal electric vehicle. This milestone marked a significant achievement in the advancement of EV technology and demonstrated Mitsubishi’s long-term commitment to sustainable transportation solutions.
CLICK ON IMAGE FOR MORE INFORMATION
Tesla: Leading the Charge Founded in 2003, Tesla Inc. became a trailblazer in the EV market. The launch of the Tesla Roadster in 2008 showcased the potential of high-performance electric cars, with a range exceeding 200 miles on a single charge. Tesla’s subsequent models, including the Model S, Model X, and Model 3, further pushed the boundaries of EV technology, making electric cars desirable, practical, and increasingly affordable.
Global Adoption of EVs The success of Tesla and early pioneers like Mitsubishi spurred significant investments in EV technology across the automotive industry. Major manufacturers like Nissan, with its Leaf model, Chevrolet, with the Bolt, and BMW, with its i3, entered the EV market. Government incentives, improved battery technology, and expanding charging infrastructure have accelerated the adoption of EVs worldwide.
CLICK ON IMAGE FOR MORE INFORMATION
Chapter 4: Pushing for Sustainability Beyond hybrid and electric vehicles, the automobile industry has embraced broader sustainability goals. This includes reducing the environmental impact of manufacturing processes, increasing the use of recyclable materials, and developing alternative fuel technologies.
Sustainable Manufacturing Practices Automakers have made significant strides in reducing the environmental footprint of their manufacturing operations. Measures include reducing energy consumption, minimizing waste, and using renewable energy sources. For instance, Ford’s Rouge Center in Michigan incorporates living roofs and solar panels, showcasing sustainable industrial practices.
Alternative Fuels and Energy Sources In addition to electric power, other alternative fuels are being explored. Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (FCVs), like the Toyota Mirai and Honda Clarity, offer another zero-emission option, with water vapor as the only byproduct. Biofuels and synthetic fuels are also being developed to provide cleaner combustion alternatives for traditional engines.
Chapter 5: The Future of Autonomous Driving One of the most exciting and transformative areas of automotive innovation is autonomous driving technology. Self-driving cars promise to revolutionize transportation, enhancing safety, reducing traffic congestion, and providing new mobility solutions.
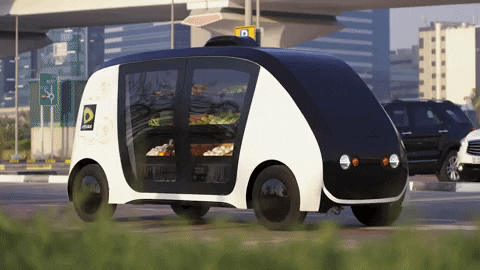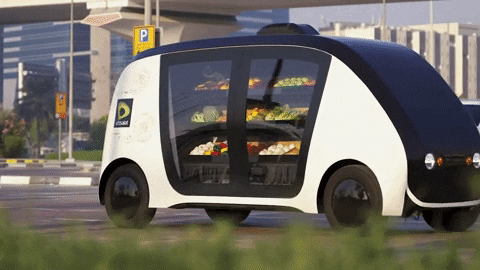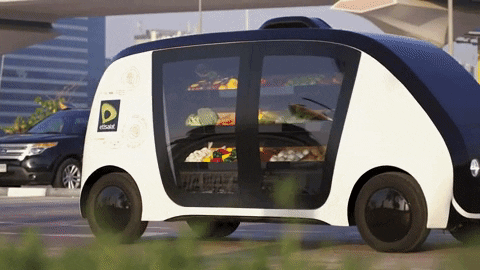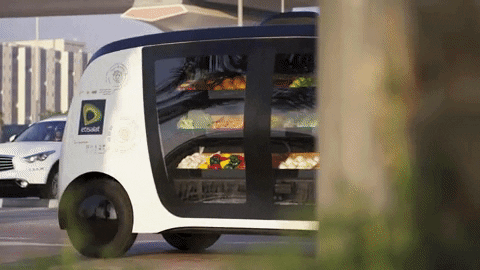
Levels of Autonomy Autonomous driving is categorized into levels, from Level 0 (no automation) to Level 5 (full automation). Currently, most commercially available vehicles with autonomous features fall into Levels 2 and 3, offering partial automation with driver supervision.
Key Players and Technological Advances Companies like Waymo (a subsidiary of Alphabet Inc.), Tesla, and traditional automakers are leading the development of autonomous driving technologies. Advances in sensors, artificial intelligence, and machine learning are critical to enabling vehicles to navigate complex environments safely and efficiently.
Challenges and Regulatory Considerations While the technology is advancing rapidly, significant challenges remain. These include ensuring safety, addressing legal and regulatory issues, and building public trust. Governments and industry stakeholders are working together to develop standards and regulations to facilitate the safe deployment of autonomous vehicles.
CLICK HERE FOR UN CLIMATE ACTION PLAN
Conclusion: A Continual Journey of Innovation The evolution of the automobile industry in response to environmental concerns and technological advances reflects a broader commitment to innovation and sustainability. From the development of hybrid and electric vehicles to the exploration of alternative fuels and the pursuit of autonomous driving, the industry is continually adapting to meet the challenges of the modern world. As we look to the future, the legacy of automotive pioneers and the ongoing dedication to progress will continue to drive transformative change, shaping the way we move and live.
Next in the Series: “Global Impact and the Road Ahead: How the Automobile Industry Shapes Our Future” In the next article of this series, we will explore the global impact of the automobile industry and the future trends shaping transportation. We’ll examine how automotive innovations are influencing global markets, urban planning, and environmental policies. Join us as we delve into how the automobile industry continues to be a driving force in shaping our world and what lies ahead on the road to sustainable, efficient, and intelligent transportation solutions.













